Lesser Bird-of-paradise
Paradisaea minor
Where is it found?
Tropical Forests
Diet and foraging method
Key adaptations
Males have brightly coloured plumage for attracting females with elaborate courtship dances.
Robust pointed bill for accessing and eating fruit, insects and snails in the dense forest canopy.
Robust pointed bill for accessing and eating fruit, insects and snails in the dense forest canopy.
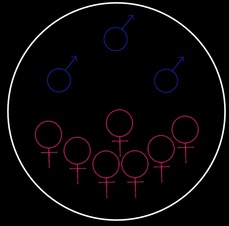
Social organisation and mating system
Solitary
Males aim to impress females in leks. Females then build nests high in the tree canopy where they incubate their eggs - up to 12 - on their own.
Did you know that...?
They may be one of the only toxic birds! Many believe that their skins contain toxins derived from their diet - insects and plants - that protect them against predators. As the birds are so colourful, the predator will remember an encounter with this toxic and bad tasting bird so are unlikely to target other birds that look the same.
Taxonomy
Sources
Maps from: http://species.mol.org/species/
Male lesser bird of paradise: "Lesser Bird of Paradise". Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons - https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lesser_Bird_of_Paradise.jpg#/media/File:Lesser_Bird_of_Paradise.jpg
Male lesser bird of paradise: "Lesser Bird of Paradise". Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons - https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Lesser_Bird_of_Paradise.jpg#/media/File:Lesser_Bird_of_Paradise.jpg